Findings and diagnosis
Findings
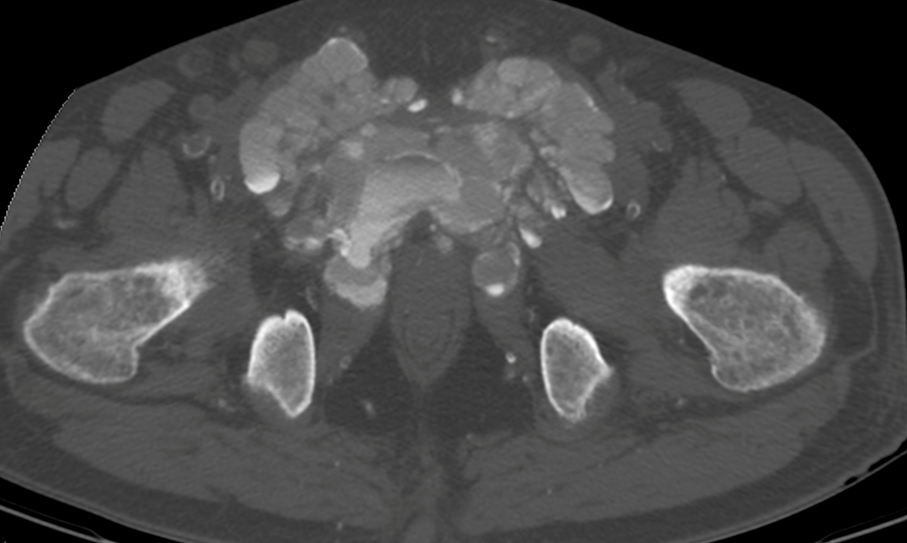
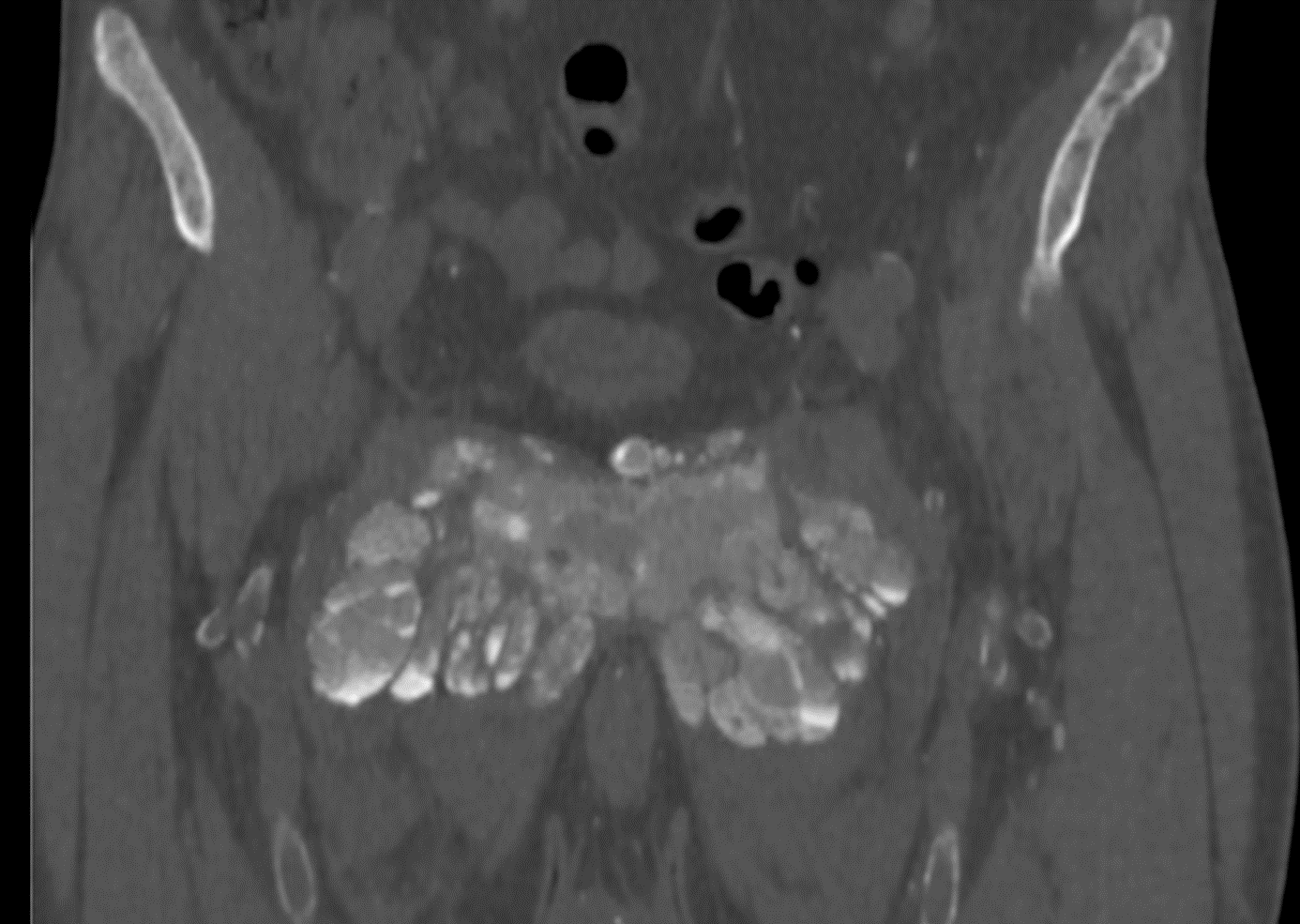
The standard radiograph of the pelvis shows a predominantly calcified medial structure projecting onto the pubic symphysis with calcifications of the soft parts of the left thigh and diffuse mediacalcosis. Pelvic CT scan shows a bilateral symmetrical mass centered on the pubic symphysis, with amorphous, dense cystic and lobulated calcifications, measuring approximately 14.4 × 9.9 cm, extending over 9.4 cm, with pubic osteolysis and massive infiltration of the adjacent muscles. Some of the cystic masses have liquid-liquid levels with calcium sedimentation.
Differential diagnosis
- Calcific tendinosis
- Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (CPPD)
- Tophaceous gout
- Calcific myonecrosis
- Tumoral calcinosis
- Myositis ossificans
- Synovial osteochondromatosis
Diagnosis: Tumoral calcinosis (tumoral calcification of chronic renal failure)
Treatment
The therapeutic management included primary measures to regulate the phosphocalcic balance; the indication of a parathyroidectomy was then justified by the secondary hyperparathyroidism and the presence of parathyroid hyperplasia on scintigraphy. The patient benefited from a total parathyroidectomy with partial regression of his symptoms.